WEB DOCUMENTS :
The documents in the WWW can be grouped into three broad categories: static, dynamic, and active. The category is based on the time the contents of the document are determined.
Static Documents :
Static documents are fixed-content documents that are created and stored in a server. The client can get a copy of the document only. In other words, the contents of the file are determined when the file is created, not when it is used. Of course, the contents in the server can be changed, but the user cannot change them. When a client accesses the document, a copy of the document is sent. The user can then use a browsing program to display the document
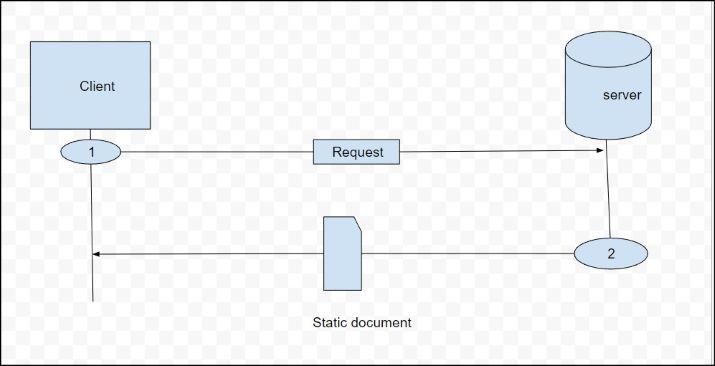
Static documents are prepared using one of the several languages: Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), Extensible Markup Language (XML), Extensible
Style Language (XSL), and Extended Hypertext Markup Language (XHTML).
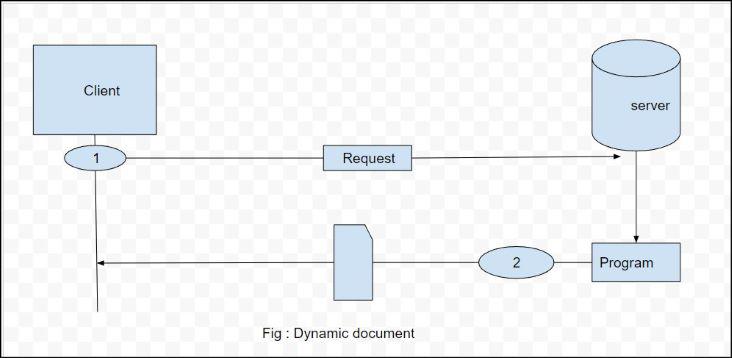
Dynamic Documents
A dynamic document is created by a Web server whenever a browser requests the document. When a request arrives, the Web server runs an application program or a script that creates the dynamic document.
The server returns the output of the program or script as a response to the browser that requested the document. Because a fresh document is created for each request, the contents of a dynamic document may vary from one request to another. A very simple example of a dynamic document is the retrieval of the time and date from a server. Time and date are kinds of information that are dynamic in that they change from moment to moment.
The client can ask the server to run a program such as the date program in UNIX and send the result of the program to the client.
Common Gateway Interface (CGI)
The Common Gateway Interface (CGI) is a technology that creates and handles dynamic documents. CGI is a set of standards that defines how a dynamic document is
written, how data are input to the program, and how the output result is used. CGI is not a new language; instead, it allows programmers to use any of several languages such as C, C++, Bourne Shell, Korn Shell, C Shell, Tcl, or Perl.
The only thing that CGI defines is a set of rules and terms that the programmer must follow.
The term common in CGI indicates that the standard defines a set of rules that is common to any language or platform. The term gateway here means that a CGI program can be used to access other resources such as databases, graphic packages, and so on.
The term interface here means that there is a set of predefined terms, variables, calls, and so on that can be used in any CGI program. A CGI program in its simplest form is code written in one of the languages supporting CGI. Any programmer who can encode a sequence of thoughts in a program and knows the syntax of one of the above mentioned languages can write a simple CGI program.
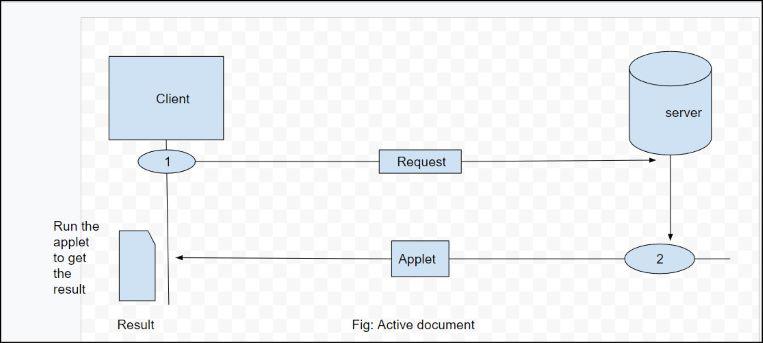
Active Documents
For many applications, we need a program or a script to be run at the client site. These are called active documents. For example, suppose we want to run a program
that creates animated graphics on the screen or a program that interacts with the user. The program definitely needs to be run at the client site where the animation or interaction takes place. When a browser requests an active document, the server sends a copy of the document or a script. The document is then run at the client (browser) site.
Java Applets
One way to create an active document is to use Java applets. Java is a combination of a high-level programming language, a run-time environment, and a class library that allows a programmer to write an active document (an applet) and a browser to run it. It
can also be a stand-alone program that doesn’t use a browser. An applet is a program written in Java on the server. It is compiled and ready to be
run. The document is in bytecode (binary) format. The client process (browser) creates an instance of this applet and runs it. A Java applet can be run by the browser in two ways. In the first method, the browser can directly request the Java applet program in
the URL and receive the applet in binary form. In the second method, the browser can retrieve and run an HTML file that has embedded the address of the applet as a tag.


No comments:
Post a Comment